96 Ratti (售价 $52.0)
Burma, Mon kingdom of Syriam (4th Century AD) Silver Unit (96 Rattis) Coin. aVF.
Mint Period: 4th Century AD Reference: Mitchiner SEA.469. R! Denominations: Silver 1 Unit (96 Rattis) Condition: A well work obverse, wakly struck reverse, dark oxidation spots in reverse, otherwise about VF. Diameter: 29mm Weight: 8.75gm Material: Silver
Obverse: Round and thick conch within beaded border.
Reverse: Weakly struck reverse or uniface issue.
The Pyu city states (Burmese: ပျူ မြို့ပြ နိုင်ငံများ) were a group of city-states that existed from c. 2nd century BCE to c. mid-11th century in present-day Upper Burma (Myanmar). The city-states were founded as part of the southward migration by the Tibeto-Burman-speaking Pyu people, the earliest inhabitants of Burma of whom records are extant. The thousand-year period, often referred to as the Pyu millennium, linked the Bronze Age to the beginning of the classical states period when the Pagan Kingdom emerged in the late 9th century.
The city-states—five major walled cities and several smaller towns have been excavated—were all located in the three main irrigated regions of Upper Burma: the Mu River Valley, the Kyaukse plains and Minbu region, around the confluence of the Irrawaddy and Chindwin Rivers. Part of an overland trade route between China and India, the Pyu realm gradually expanded south. Halin, founded in the 1st century AD at the northern edge of Upper Burma, was the largest and most important city until around the 7th or 8th century when it was superseded by Sri Ksetra (near modern Pyay) at the southern edge. Twice as large as Halin, Sri Ksetra was the largest and most influential Pyu centre.
The Pyu culture was heavily influenced by trade with India, importing Buddhism as well as other cultural, architectural and political concepts, which would have an enduring influence on the Culture of Burma and political organisation. The Pyu calendar, based on the Buddhist calendar, later became the Burmese calendar. Recent scholarship, though yet not settled, suggests that the Pyu script, based on the Indian Brahmi script, may have been the source of the Burmese script used to write the Burmese language.
The millennium-old civilisation came crashing down in the 9th century when the city-states were destroyed by repeated invasions from the Kingdom of Nanzhao. The Bamar people, who came from Nanzhao, set up a garrison town at Bagan at the confluence of the Irrawaddy and Chindwin Rivers. Pyu settlements remained in Upper Burma for the next three centuries but the Pyu gradually were absorbed into the expanding Pagan Kingdom. The Pyu language still existed until the late 12th century. By the 13th century, the Pyu had assumed the Burman ethnicity. The histories and legends of the Pyu were also incorporated to those of the Bamar.
Only the city-states of Halin, Beikthano and Sri Ksetra are designated as UNESCO World Heritage Sites, where the other sites can be added in the future for an extension nomination.
Only 1$ shipping for each additional coin purchased!
1 Franc 比利时 銀 利奥波德二世 (比利时)
本组有 12 钱币 / 10 售价
⇑
5 Yuan 中华人民共和国 銀
本组有 2 钱币
⇑





 Deutsch
Deutsch Русский
Русский Українська
Українська English
English Italiano
Italiano Français
Français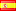 Español
Español 汉语
汉语














