Origin of the name for Chinese Yuan
The origin of the name "Yuan" as the monetary unit of China dates back to ancient times and has undergone various historical developments. The term "Yuan" (元) is derived from Chinese characters and has multiple meanings and interpretations. Here are some possible origins and meanings of the name "Yuan" for the monetary unit:
Meaning "Round" or "Circular": The Chinese character "Yuan" (元) can mean "round" or "circular" in Mandarin Chinese. This interpretation reflects the shape of ancient Chinese coins, which were typically round with a square hole in the center. These coins were known as "Yuanbao" (元寶), and the term "Yuan" came to be associated with currency and wealth.
Symbolizing Unity or Origin: In ancient Chinese philosophy and cosmology, the concept of "Yuan" (原) can represent the origin, source, or fundamental principle of existence. The use of "Yuan" as a monetary unit may symbolize the unity and foundational role of currency in economic transactions and societal organization.
Historical Usage: The term "Yuan" has been used historically to refer to various forms of currency in China, including coins, banknotes, and units of account. It has been employed by different dynasties and regimes throughout Chinese history to denote their respective currencies.
Modern Adoption: The modern adoption of the name "Yuan" as the official currency of the People's Republic of China dates back to the mid-20th century. In 1948, the Chinese Nationalist government introduced the "Yuan" as the official currency of the Republic of China. After the establishment of the People's Republic of China in 1949, the name "Yuan" was retained for the new socialist currency system.
Overall, the name "Yuan" for the Chinese monetary unit has deep historical and cultural roots, reflecting various meanings and interpretations within Chinese language, philosophy, and society. Its adoption as the official currency of China underscores its significance as a symbol of economic prosperity, unity, and continuity throughout Chinese history.
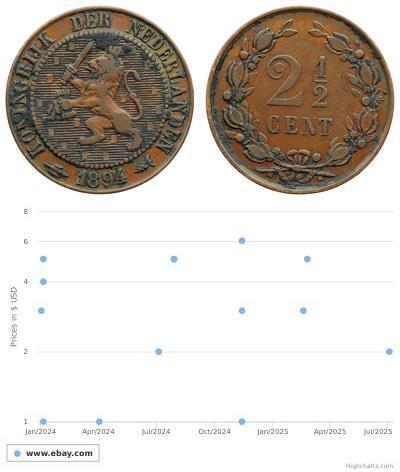
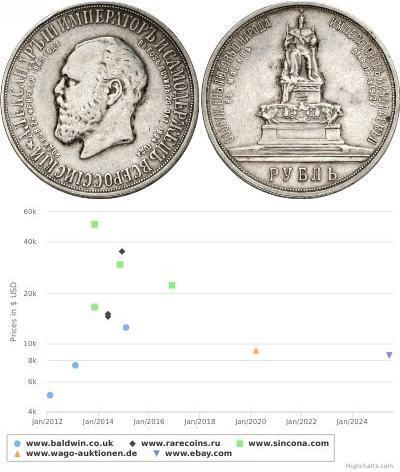
You may be interested in following coins
2025-06-16
- Historical Coin Prices
2025-05-29
- Historical Coin Prices