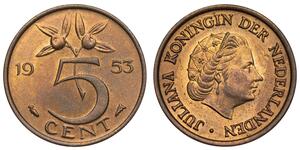Coins mint during the reign of Constantine the Great
Constantine the Great, also known as Constantine I, was Roman Emperor from 306 to 337 AD. During his reign, coins were minted across the Roman Empire bearing his image and various inscriptions. Constantine's coinage is significant for several reasons:
Adoption of Christianity: Constantine's reign marked a pivotal moment in Roman history with the Edict of Milan in 313 AD, which legalized Christianity. Some of his coins feature Christian symbols such as the Chi-Rho monogram or references to Christianity, reflecting his conversion to the faith.
Christianization of Roman Coinage: Constantine's coinage played a role in the early Christianization of Roman society. While earlier Roman coins typically featured pagan gods and symbols, Constantine's coins introduced Christian imagery and inscriptions, reflecting the growing influence of Christianity within the Empire.
Religious Syncretism: Despite his conversion to Christianity, Constantine's coinage continued to incorporate traditional Roman religious imagery alongside Christian symbols. This reflects the period of religious transition during Constantine's reign, where elements of both pagan and Christian beliefs coexisted.
Iconography: Constantine's coinage often depicted his portrait on the obverse (front) and various symbolic representations on the reverse (back). These symbols included military imagery, personifications of virtues or concepts, and sometimes Christian symbols such as the Chi-Rho or a cross.
Mint Locations: Coins bearing Constantine's image were minted across the Roman Empire, including mints in Rome, Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul), Trier (in modern-day Germany), Nicomedia (in modern-day Turkey), and other provincial mints.
Coin Denominations: Constantine's coinage encompassed a variety of denominations, including gold aurei, silver denarii, and bronze folles. The denomination and metal composition of the coins varied depending on factors such as location, economic conditions, and the intended use of the coins.
Constantine's coinage is highly sought after by collectors due to its historical significance and the role it played in the transition of the Roman Empire towards Christianity. These coins provide valuable insights into the religious, political, and cultural developments of the time.
You may be interested in following coins
2025-05-24
- New coin is added to 5 Cent Kingdom of the Netherlands (1815 - ) Bronze
5 Cent Kingdom of the Netherlands (1815 - ) Bronze
group has 7 coins / 7 prices
⇑
Netherlands - 5 Cents 1953 - Juliana, High Quality
2025-05-25
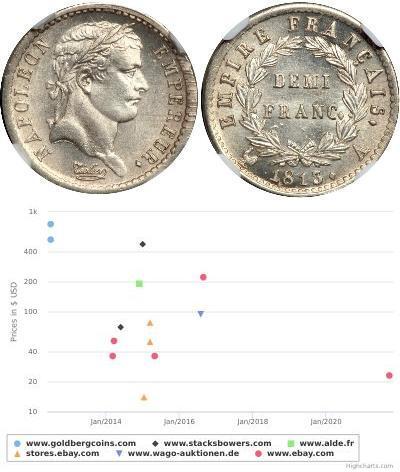
- Historical Coin Prices




-300-150-VITBwcI0OHQAAAEqPTlDRaZv.jpg)