(Verkauft für $43.0)
1576, Bohemia, Maximilian II. Silver White Grossus (Weissgroschen) Joachimsthal!
Mint Period: 1576 Condition: About XF! Mint Place. Joachimsthal Reference: Dietiker 176. Rare! Denomination: White Grossus ("Weissgroschen") / Bily gros Diameter: 21mm Weight: 1.29gm Material: Silver
Obverse: Crowned Bohemian rampart lion left. Legend: MAXI . II . DE . G . RO . IMS . A . GER . H . B . REX Reverse: Crown above double-headed imperial eagle with crowned shield at chest. Legend: ARCH . DVX . AVS . DVX . BVH . MA . MO . 76
Maximilian II (31 July 1527 – 12 October 1576), a member of the Austrian House of Habsburg, was Holy Roman Emperor from 1564 until his death. He was crowned King of Bohemia in Prague on 14 May 1562 and elected King of Germany (King of the Romans) on 24 November 1562. On 8 September 1563 he was crowned King of Hungary and Croatia in the Hungarian capital Pressburg (Pozsony in Hungarian; now Bratislava, Slovakia). On 25 July 1564 he succeeded his father Ferdinand I as ruler of the Holy Roman Empire.
Maximilian's rule was shaped by the confessionalization process after the 1555 Peace of Augsburg. Though a Habsburg and a Catholic, he approached the Lutheran Imperial estates with a view to overcome the denominational schism, which ultimately failed. He also was faced with the ongoing Ottoman–Habsburg wars and rising conflicts with his Habsburg Spain cousins.
According to Fichtner, he failed to achieve his three major aims: rationalizing the government structure, unifying Christianity, and evicting the Turks from Hungary.
Born in Vienna, Austria, he was the eldest son of the Habsburg archduke Ferdinand I, younger brother of Emperor Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, and the Jagiellonian princess Anne of Bohemia and Hungary (1503–1547). He was named after his great-grandfather, Emperor Maximilian I. At the time of his birth, his father Ferdinand succeeded his brother-in-law King Louis II in the Kingdom of Bohemia and the Kingdom of Hungary, laying the grounds for the global Habsburg Monarchy.
Having spent his childhood years at his fathers's court in Innsbruck, Tyrol, he was educated principally in Italy. Among his teachers were humanist scholars like Kaspar Ursinus Velius and Georg Tannstetter. Maximilian also came in contact with the Lutheran teaching and early on corresponded with the Protestant prince Augustus of Saxony, suspiciously eyed by his Habsburg relatives. From the age of 17, he gained some experience of warfare during the Italian War campaign of his uncle Charles V against King Francis I of France in 1544, and also during the Schmalkaldic War. Upon Charles' victory in the 1547 Battle of Mühlberg, Maximilian put in a good word for the Schmalkaldic leaders Elector John Frederick I of Saxony and Landgrave Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse, and soon began to take part in Imperial business.
On 13 September 1548 Emperor Charles V married Maximilian to Charles's daughter (Maximilian's cousin) Mary of Spain in the Castile residence of Valladolid. By the marriage his uncle intended to strengthen the ties with the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs, but also to consolidate his nephew's Catholic faith. Maximilian temporarily acted as the emperor's representative in Spain, however not as stadtholder of the Habsburg Netherlands as he had hoped for. To his indignation, King Ferdinand appointed his younger brother Ferdinand II administrator in the Kingdom of Bohemia, nevertheless Maximilian's right of succession as the future king was recognised in 1549. He returned to Germany in December 1550 in order to take part in the discussion over the Imperial succession.
Maximilian's relations with his uncle worsened, as Charles V, again embattled by rebellious Protestant princes led by Elector Maurice of Saxony, wished his son Philip II of Spain to succeed him as emperor. However, Charles' brother Ferdinand, who had already been designated as the next occupant of the imperial throne, and his son Maximilian objected to this proposal. Maximilian sought the support of the German princes such as Duke Albert V of Bavaria and even contacted Protestant leaders like Maurice of Saxony and Duke Christoph of Württemberg. At length a compromise was reached: Philip was to succeed Ferdinand, but during the former's reign Maximilian, as King of the Romans, was to govern Germany. This arrangement was not carried out, and is only important because the insistence of the emperor seriously disturbed the harmonious relations which had hitherto existed between the two branches of the Habsburg family; an illness which befell Maximilian in 1552 was attributed to poison given to him in the interests of his cousin and brother-in-law, Philip II of Spain.
The relationship between the two cousins was uneasy. While Philip had been raised a Spaniard and barely travelled out of the kingdom during is life, Maximilian identified himself as the quintessential German prince and often displayed a strong dislike of Spaniards, whom he considered as intolerant and arrogant. While his cousin was reserved and shy, Maximilian was outgoing and charismatic. His adherence to humanism and religious tolerance put him at odds with Philip who was more committed to the defence of the Catholic faith. Also, he was considered a promising commander, while Philip disliked war and only once did he personally command an army. Nonetheless, the two remained committed to the unity of their dynasty.
In 1551 Maximilian attended the Council of Trent and the next year took up his residence at Hofburg Palace in Vienna, celebrated by a triumphal return into the city with a large entourage including the elephant Suleiman. While his father Ferdinand concluded the 1552 Treaty of Passau with the Protestant estates and finally reached the Peace of Augsburg in 1555, Maximilian was engaged mainly in the government of the Austrian hereditary lands and in defending them against Ottoman incursions. In Vienna, he had his Hofburg residence extended with the Renaissance Stallburg wing, the site of the later Spanish Riding School, and also ordered the construction of Neugebäude Palace in Simmering. The court held close ties to the University of Vienna and employed scholars like the botanist Carolus Clusius and the diplomat Ogier Ghiselin de Busbecq. Maximilian's library curated by Hugo Blotius later became the nucleus of the Austrian National Library. He implemented the Roman School of composition with his court orchestra, however, his plans to win Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina as Kapellmeister foundered on financial reasons. In the 1550s, Vienna had more than 50,000 inhabitants, making it the largest city in Central Europe with Prague and before Nuremberg (40,000 inhabitants).
The religious views of the future King of Bohemia had always been somewhat uncertain, and he had probably learned something of Lutheranism in his youth; but his amicable relations with several Protestant princes, which began about the time of the discussion over the succession, were probably due more to political than to religious considerations. However, in Vienna he became very intimate with Sebastian Pfauser (de), a court preacher influenced by Heinrich Bullinger with strong leanings towards Lutheranism, and his religious attitude caused some uneasiness to his father. Fears were freely expressed that he would definitely leave the Catholic Church, and when his father Ferdinand became emperor in 1558 he was prepared to assure Pope Paul IV that his son should not succeed him if he took this step. Eventually Maximilian remained nominally an adherent of the older faith, although his views were tinged with Lutheranism until the end of his life. After several refusals he consented in 1560 to the banishment of Pfauser, and began again to attend the Masses of the Catholic Church.
In November 1562 Maximilian was chosen King of the Romans, or German king, by the electoral college at Frankfurt, where he was crowned a few days later, after assuring the Catholic electors of his fidelity to their faith, and promising the Protestant electors that he would publicly accept the confession of Augsburg when he became emperor. He also took the usual oath to protect the Church, and his election was afterwards confirmed by the papacy. He was the first King of the Romans not to be crowned in Aachen. In September 1563 he was crowned King of Hungary by the Archbishop of Esztergom, Nicolaus Olahus, and on his father's death, in July 1564, he succeeded to the empire and to the kingdoms of Hungary, Croatia and Bohemia.
The new emperor had already shown that he believed in the necessity for a thorough reform of the Church. He was unable, however, to obtain the consent of Pope Pius IV to the marriage of the clergy, and in 1568 the concession of communion in both kinds to the laity was withdrawn. On his part Maximilian granted religious liberty to the Lutheran nobles and knights in Austria, and refused to allow the publication of the decrees of the council of Trent. Amidst general expectations on the part of the Protestants he met his first Diet of Augsburg in March 1566. He refused to accede to the demands of the Lutheran princes; on the other hand, although the increase of sectarianism was discussed, no decisive steps were taken to suppress it, and the only result of the meeting was a grant of assistance for the Turkish War, which had just been renewed. Collecting a large army Maximilian marched to defend his territories; but no decisive engagement had taken place when a truce was made in 1568, and the emperor continued to pay tribute to the sultan as the price of peace in the western and northern areas of the Hungarian kingdom still under Habsburg control.
Meanwhile, the relations between Maximilian and Philip of Spain had improved; and the emperor's increasingly cautious and moderate attitude in religious matters was doubtless because the death of Philip's son, Don Carlos, had opened the way for the succession of Maximilian, or of one of his sons, to the Spanish throne. Evidence of this friendly feeling was given in 1570, when the emperor's daughter, Anna, became the fourth wife of Philip; but Maximilian was unable to moderate the harsh proceedings of the Spanish king against the revolting inhabitants of the Netherlands. In 1570 the emperor met the diet of Speyer and asked for aid to place his eastern borders in a state of defence, and also for power to repress the disorder caused by troops in the service of foreign powers passing through Germany. He proposed that his consent should be necessary before any soldiers for foreign service were recruited in the empire; but the estates were unwilling to strengthen the imperial authority, the Protestant princes regarded the suggestion as an attempt to prevent them from assisting their co-religionists in France and the Netherlands, and nothing was done in this direction, although some assistance was voted for the defense of Austria. The religious demands of the Protestants were still unsatisfied, while the policy of toleration had failed to give peace to Austria. Maximilian's power was very limited; it was inability rather than unwillingness that prevented him from yielding to the entreaties of Pope Pius V to join in an attack on the Turks both before and after the victory of Lepanto in 1571; and he remained inert while the authority of the empire in north-eastern Europe was threatened.
In 1575, Maximilian was elected by the part of Polish and Lithuanian magnates to be the King of Poland in opposition to Stephan IV Bathory, but he did not manage to become widely accepted there and was forced to leave Poland.
Maximilian died on 12 October 1576 in Regensburg while preparing to invade Poland. On his deathbed he refused to receive the last sacraments of the Church. He is buried in St. Vitus Cathedral in Prague.
By his wife Maria he had a family of nine sons and six daughters. He was succeeded by his eldest surviving son, Rudolf, who had been chosen king of the Romans in October 1575. Another of his sons, Matthias, also became emperor; three others, Ernest, Albert and Maximilian, took some part in the government of the Habsburg territories or of the Netherlands, and a daughter, Elizabeth, married Charles IX of France.
Maximilian's policies of religious neutrality and peace in the Empire afforded its Roman Catholics and Protestants a breathing-space after the first struggles of the Reformation. His reign also saw the high point of Protestantism in Austria and Bohemia and unlike his successors, Maximilian did not try to suppress it.
He disappointed the German Protestant princes by his refusal to invest Lutheran administrators of prince-bishoprics with their imperial fiefs. Yet on a personal basis he granted freedom of worship to the Protestant nobility and worked for reform in the Roman Catholic Church, including the right of priests to marry. This failed because of Spanish opposition.
Maximilian II was a member of the Order of the Golden Fleece.

|
Beigetragen von:
anonymous 2021-03-17 |

6 Grosh Polen-Litauen (1569-1795) Silber ...
Diese Gruppe hat 4 Münzen / 4 Preise
Add coin to this group

1/4 Thaler Polen-Litauen (1569-1795) Sil ...
Diese Gruppe hat 12 Münzen / 8 Preise
Add coin to this group

1 Patagon Spanische Niederlande (1581 - ...
Diese Gruppe hat 14 Münzen / 14 Preise
Add coin to this group

1/4 Thaler Polen-Litauen (1569-1795) Sil ...
Diese Gruppe hat 2 Münzen / 2 Preise
Add coin to this group

1 Gold Shield Heiliges Römisches Reich ( ...
Diese Gruppe hat 2 Münzen / 1 Preise
Add coin to this group
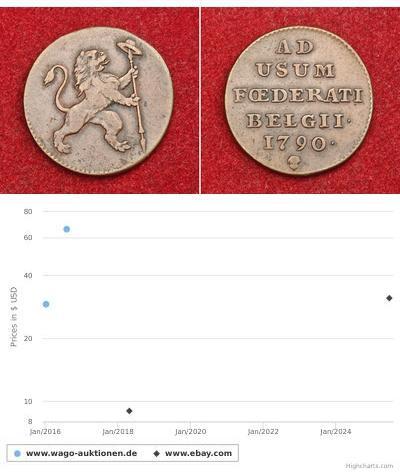
1 Duit Niederlande Kupfer
Diese Gruppe hat 18 Münzen / 17 Preise
⇑